Page 82 - NZ Herefords Magazine 2019 Edition
P. 82
Industry Focus
Hereford Single-Step
BREEDPLAN Update
WORDS / PHOTOGRAPHS CATRIONA MILLEN, SOUTHERN BEEF TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
WHEN THE MID-OCTOBER 2017 BREEDPLAN analysis was 1) Average EBVs have not changed
released, the Hereford breed in Australia, New Zealand and For most of the Hereford traits, the average EBV has not
Namibia became the first breed worldwide to implement a multi- changed between the two runs. In several traits there were
country Single-Step BREEDPLAN analysis. The introduction of very minimal changes, in the order of +/-0.1. The fact that
Single-Step BREEDPLAN meant that pedigree, performance and the average EBV remained the same is not unexpected;
genomic (DNA) information was being combined together in the while genotype information changes what we know about the
multi-trait analysis, and genomic information was contributing individual, it does not change the performance data on which
to the EBV and accuracy calculations of genotyped Hereford the EBVs are based.
animals and their relatives. In this article, we will examine what While the average EBV has not changed, this does not mean
lessons have been learnt in the 12 months since the roll out of that the EBVs for individual animals have not changed. The EBVs
Single-Step BREEDPLAN in Herefords. for some animals have changed (up or down), sometimes quite
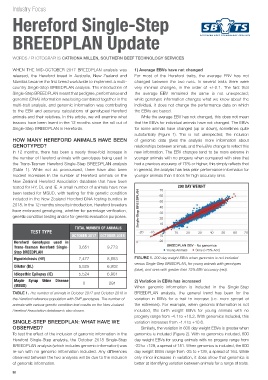
substantially (Figure 1). This is not unexpected; the inclusion
HOW MANY HEREFORD ANIMALS HAVE BEEN of genomic data gives the analysis more information about
GENOTYPED? relationships between animals, and the EBVs change to reflect this
In 12 months, there has been a nearly three-fold increase in new information. The EBV changes tend to be more extreme in
the number of Hereford animals with genotypes being used in younger animals with no progeny when compared with sires that
the Trans-Tasman Hereford Single-Step BREEDPLAN analysis had a previous accuracy of 75% or higher; this simply reflects that
(Table 1). While not as pronounced, there have also been in general, the analysis has less prior performance information for
modest increases in the number of Hereford animals on the younger animals than it does for high accuracy sires.
New Zealand Hereford Association database that have been
tested for HY, DL and IE. A small number of animals have now 200 DAY WEIGHT
been tested for MSUD, with testing for this genetic condition 70
included in the New Zealand Hereford DNA testing bundles in 60
2018. In the 12 months since its introduction, Hereford breeders 50
40
have embraced genotyping, whether for parentage verification, Single-Step BREEDPLAN 30
genetic condition testing and/or for genetic evaluation purposes. 20
TOTAL NUMBER OF ANIMALS 10
TEST TYPE -20 -10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
OCTOBER 2017 OCTOBER 2018 -10
Hereford Genotypes used in -20
Trans-Tasman Hereford Single- 3,651 9,773 BREEDPLAN EBV - No genomics
Step BREEDPLAN Young Animals Sires (>75% Acc)
Hypotrichosis (HY) 7,477 8,853 FIGURE 1. 200 day weight EBVs when genomics is not included
versus Single-Step BREEDPLAN, for young animals with genotypes
Dilutor (DL) 5,525 6,902
(blue), and sires with greater than 75% EBV accuracy (red).
Idiopathic Epilepsy (IE) 5,524 6,901
Maple Syrup Urine Disease 2) Variation in EBVs has increased
(MSUD) 0 291 When genomic information is included in the Single-Step
TABLE 1. The number of animals in October 2017 and October 2018 in BREEDPLAN analysis, the general trend has been for the
the Hereford reference population with SNP genotypes. The number of variation in EBVs for a trait to increase (i.e. more spread at
animals with various genetic condition test results on the New Zealand the extremes). For example, when genomic information is not
Hereford Association database is also shown. included, the birth weight EBVs for young animals with no
progeny range from -4.1 to +10.2. With genomics included, this
SINGLE-STEP BREEDPLAN: WHAT HAVE WE variation increases from -4.4 to +10.6.
OBSERVED? Similarly, the variation in 600 day weight EBVs is greater when
To test the effect of the inclusion of genomic information in the genomics is included (Figure 2). With no genomics included, 600
Hereford Single-Step analysis, the October 2018 Single-Step day weight EBVs for young animals with no progeny range from
BREEDPLAN analysis (which includes genomic information) was -22 to +129, a spread of 151. When genomics is included, the 600
re-run with no genomic information included. Any differences day weight EBVs range from -25 to +139, a spread of 164. While
observed between the two analyses will be due to the inclusion only minor increases in variation, it does show that genomics is
of genomic information. better at identifying variation between animals for a range of traits.
80